Communication
Even if it is a school district, a bank, a transportation system or a manufacturing plant, effective communication is essential.
What is communication?
Communication can be defined as the transferring of information and understanding between people through symbols with meaning.
Communication in any circumstance in our lives is of vital importance to be able to express our objectives, necessities, emotions, etc. It also becomes imperative in enterprises, and thus, we can mention some of its benefits:
· Establishing and diffusing the purposes and goals of the enterprise.
· Developing plans to achieve such purposes.
· Organizing human resources in an effective manner.
· Selecting, developing and evaluating the members of such enterprise.
· Originating an environment of ample participation.
· Controlling the performance of its members.
· Influencing in the motivation of our workers.
The process of communication.
To carry out effective communication, it is necessary that in the flow of ideas transmission, several elements intervene, which are described as:
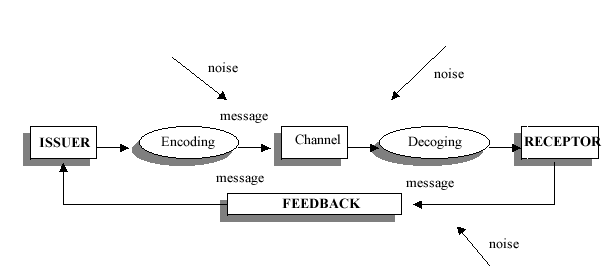
1. Transmitter (codifier): source of information and initiator of the communication process. It is his responsibility to chose the type of message and more effective channel, through which he codifies his message. In an enterprise, it will be the person who has a piece of information, necessities or desires and the intention of communicating them to one or more people.
The codification consists in the translation of information to a series of symbols for communication. This is necessary because the information can only be transmitted from one person to another through representations or symbols.
2. Receptor (de-codifier): it is the individual that receives, through his senses, the message from the transmitter.
De-codification is the interpretation and translation of a message for the message to make any sense. One of the main requirements the receptor must cover is the capability of listening. Listening is the act of paying attention to a message, not only hearing it.
Guidelines for an effective listening:
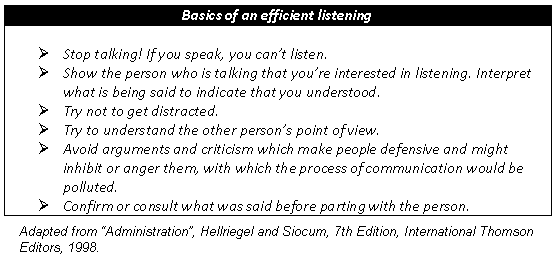
3. Message: it is the codified information the transmitter send to the receptor. The message can be given in any susceptible form to be captured and understood by one or more senses of the receptor.
4. Channels: it is the means of communication between the transmitter and the receptor, something like what air is for words and paper is for letters.
5. Feedback: it is the answer from the receptor to the message from the transmitter. It is the best way to prove that the message was received and understood.
6. Perception: it is the meaning attributed to a message by a transmitter or a receptor. Perceptions are influenced by what the individual sees, by the way he organizes these elements in his memory and by the meanings attributed to them.
DIAGRAM OF COMMUNICATION PROCESS.
Barriers in Communication.
They are the conditions or factors that interfere in the effective transmission of a message, and among them we find:
Interpersonal Barriers.
· The interpretation of the message made by the receptor.
· Physiological defects of the receptor or transmitter.
· The emotions and feelings of the transmitter or receptor.
· The environmental conditions in which the message is given.
· The use of semantics, such as differences in language, inadequate words, insufficient information, etc.
Organizational Barriers.
When an enterprise grows, its organic structure widens too much, originating communication problems. With it, problems like when a message is overdone, modified, eliminated or changed, even more when the message was transmitted orally.
Another barrier is translated in administrative authority, where we must remember that authority is a characteristic of every enterprise. This means this supervision generates a barrier. Finally, specialization is another barrier that affects communication effectiveness.

