TRANSLATIONS IN THE PLANE.
Translation is the action of changing the position of a shape in the plane. We are translating a shape to a specific distance, direction and sense in the plane.
8.18 Translate a triangle to another part of the plane using a vector as a guide.
Solution:
Follow this procedure step-by-step:
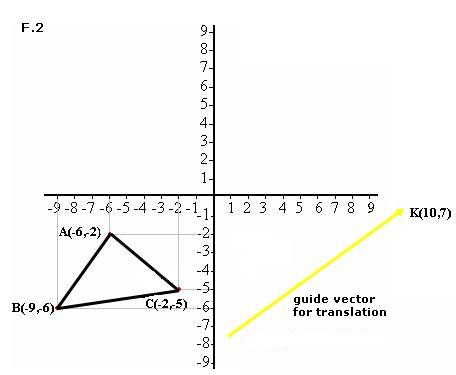
1º In a sheet of paper, draw a coordinate axis as the one you have in F.1. Mark the following points or coordinates: (-6,-2), (-9,-6) and (-2,-5), which will be the vertices of the triangle.
2º Join points ABC of the triangle and trace a guide vector for this translation, you see it in yellow. Notice that the terminal point of this vector has the components (10,7).
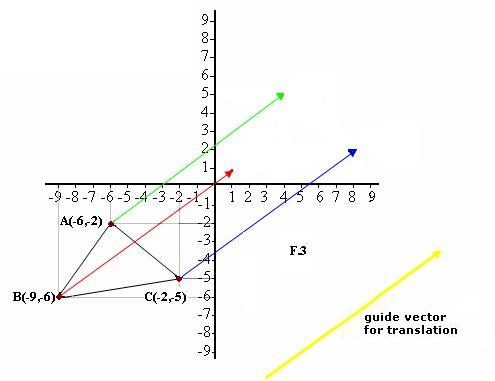
A simple way of translating a shape is by using a guide vector. To do this, we trace the guide vector to each point of triangle ABC keeping the same magnitude, direction and sense of the guide vector. You can see this in F.3 in green, red, and blue.
The terminal points of the green, red and blue vectors are the new triangle vertices. If we add the components of each point A, B and C with those of the guide vector, we will get the corresponding points of the new triangle.
We will represent the terminal point of A as A’, the terminal point of B as B’, and the terminal point of C as C’, just as you see in F.4.
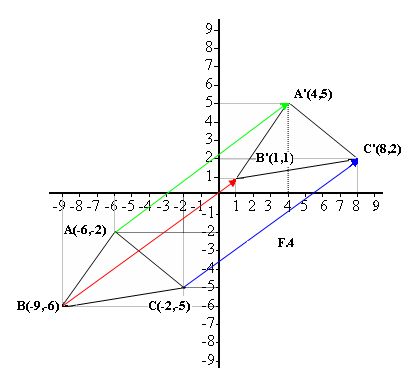
Triangle ABC has transformed into triangle A’B’C’ in relation to the guide vector. Thus, the vectors that join ABC with A’B’C’ have the same magnitude, direction and sense.
Points A’,B’ and C’ are the equivalent counterparts of A, B and C. In other words, they are located in the same order or position.
If we add the components of point A = (–6, –2) with the components of the guide vector (10,7), we will get the components of point A’ (–6 + 10, –2 + 7) = A’(4,5).
If we add the components of point B = (–9, –6) with the components of the guide vector (10,7), we will get the components of point B’ (–9+ 10, –6+ 7) = B’(1,1).
If we add the components of point C = (–2, –5) with the components of the guide vector (10,7), we will get the components of point C’ (–2+ 10, –5+ 7) = C’(8,2).
