Production Function
Production function determines the amount companies
are going to produce, that's to say, the quantity of goods and
services that they are going to offer the market.
Every company has:
Productive resources
or capital stock (machines, computers, vehicles, etc).
Human resources (workers)
We can represent the production function using
the formula y = F (L,K). The production of a country (Y) depends
on the amount of work (L) and the quantity of capital (K).
The amount of work is determined
in the work market, whilst the productive resources are considered
fixed in the short term.
With these two premises we can now draw the
curve of production function.
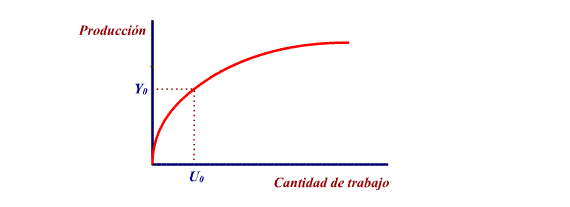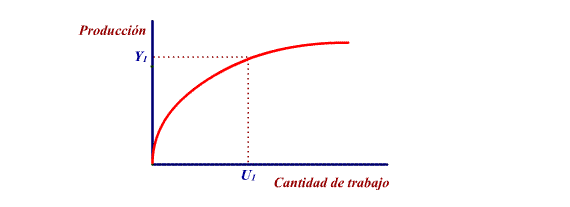
The slope of the curve is positive but decreasing:
the greater the volume of work the greater the rate of production
but with an increasingly lower percentage (performance law).
For example: a house can be built
quicker with two workmen than with one, and with 4 rather than
2, but there will be a moment when it will not be worth bringing
in more workmen.
A variation in the volume of employment (given
a determined quantity of productice resources) causes a movement
along the curve.
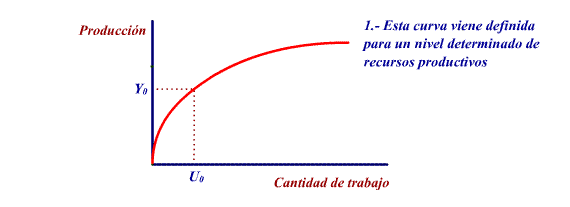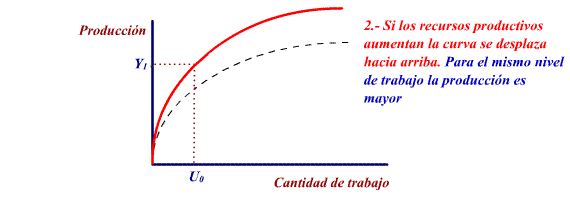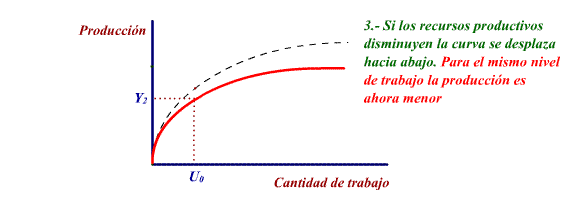
A variation in the volume of the productive
resources can cause a movement in the curve:
If the productive resources increase
for a determined level of work, the level of production will
increase: the production curve will move up.
If the productive resources decrease
the production curve moves down.
The productive resources an
economy has are determined by their level of savings:
The higher the level of savings the
more a country will invest, which in the long term will increase
their productive resources and therefore, their level of production.
In short, the work market determines the level
of employment in the economy and once this has been defined, the
production function will determine the volume of production (aggregate
supply).
The Production function that
we have analysed can get complicated if we introduce more productive
factors:
Natural Resources (N) that
a country has: minerales, fish, woods, energy, etc.
Human Capital (H): a populations'
level of training and abilities.
The Production Function will
now remain: Y = f (L, K, N, H),
working in a very similar way to that we have already explained:
Change of (L): movement along
the curve.
Change of (K, H, N): movements
in the curve.

