Aggregate offer-demand outline
The position at which the offer and demand
curves cross determines the
level of production and prices for
the economy to be in a state of
equilibrium. The position also
determined the level of employment.
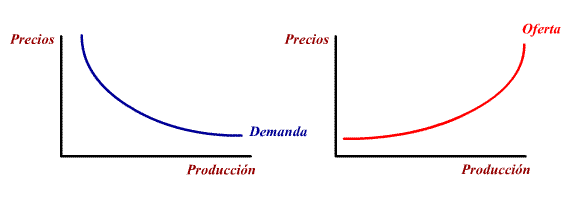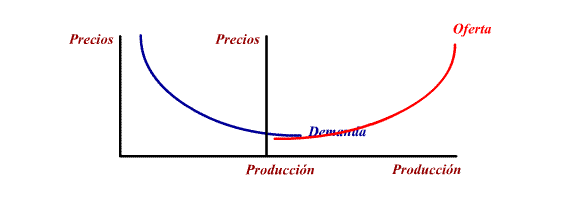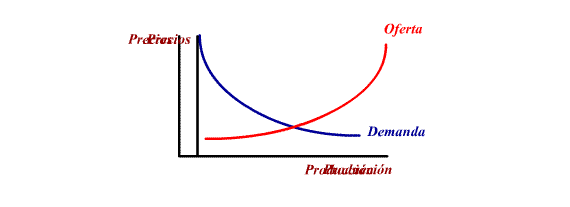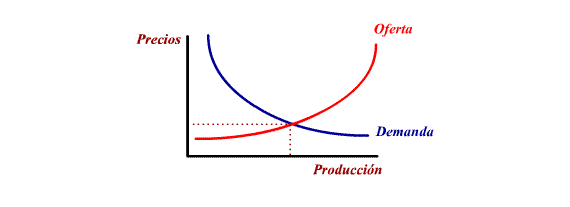
What happens if the economy is not in equilibrium?
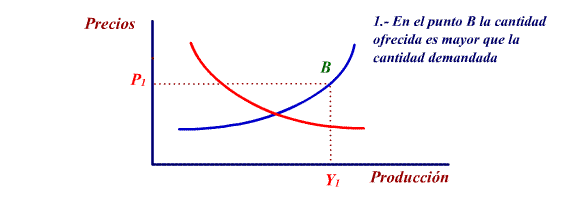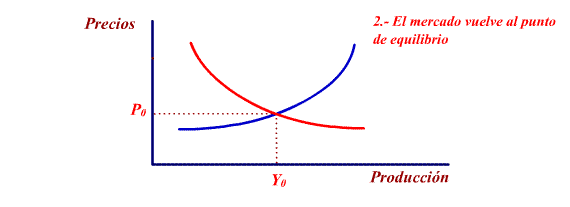
Let's suppose that offer is greater
than demand (point B). This implies that part of a company's
production is not sold. In order not to remain with a part of
the production in the warehouse they start to lower their prices
(which will increase demand) and at the same time they will
reduce production.
This process continues until the
economy finds itself in a state of equilibrium:
Quanity
offered = Quantity demanded
Let's suppose now that the offer
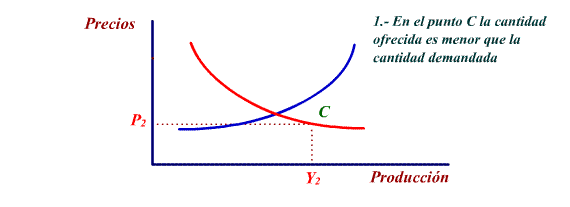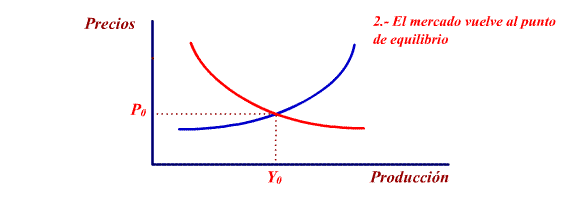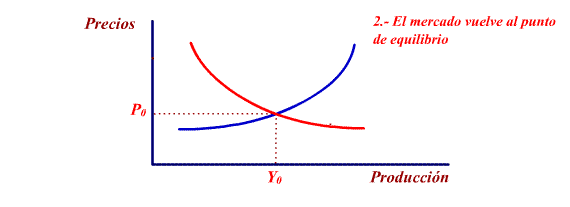
is less than demand (point C). Part of the citizen's demands
will not be met which will cause prices to rise. Companies will
increase their production to attend to demand. The process continues
again until the economy reaches a state of equilibrium.
|


