|
|
|
|
Economic Theories, Fiscal and Monetary
Policies
Classic Model
a) Demand Management
Monetary Expansion: this
produces the monetary offer curve to move towards the right,
which means a decrease in interest rates and therefore, an
increase in investments. This makes the Aggregate Demand curve
also move towards the right.
Given that the Aggregate Offer
curve is vertical, balanced production remains constant and
it will produce an increase in prices.
Fiscal Expansion: increase
in public expenditure or decrease in taxes (T) will make the
aggregate demand curve move towards the right. Again this
will produce an increase in prices, whilst the level of production
maintains constant.
The increase in prices makes the
monetary offer (measure in real terms) contract and as a result
interest rates increase, making investment fall. At the end
of the process, public expenditure is compensated with a decrease
in investment.
b) Offer policies
They include, amongst others, measures
destined to increase the amount of jobs (for example: reduction
of taxes which record work income). This causes the work offer
curve to move right, increasing the level of full employment
and therefore, the production offered by the companies.
The aggregate offer curve moves
towards the right making prices decrease. This in turn causes
an expansion of the monetary offer in real terms, which makes
interest rates decrease and which makes investments increase
(the aggregate demand curve also moves towards the right).
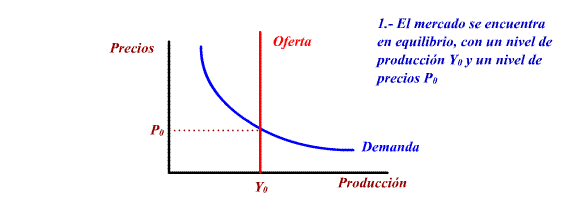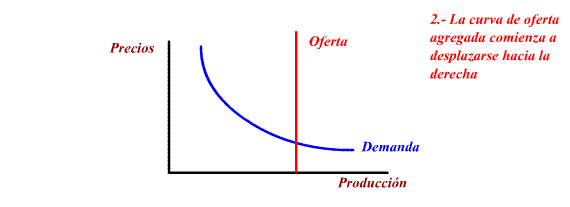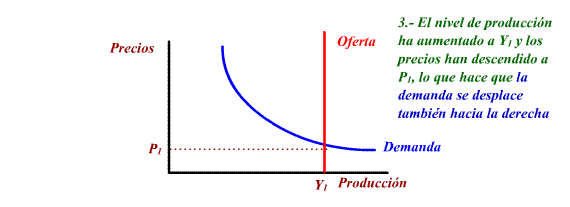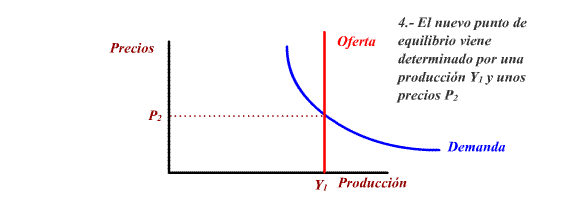
Other measures of the offer policy
include different interventions that help promote technological
innovations, which cause the production curve to move up (for
the same level of employment, the production carried out is
greater), which also provokes the aggregate offer curve to
move towards the right.
From here, the same process is
repeated.
Keynesian Model
a) Demand Policies
Monetary Expansion: causes
the monetary offer to move towards the right, producing a
decrease in interest rates and an increase in investments:
the aggregate demand moves towards the right.
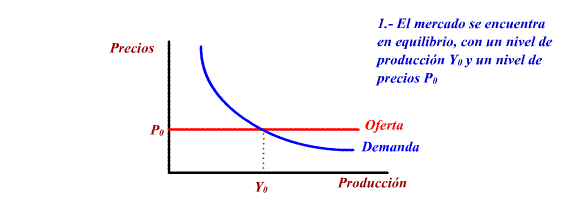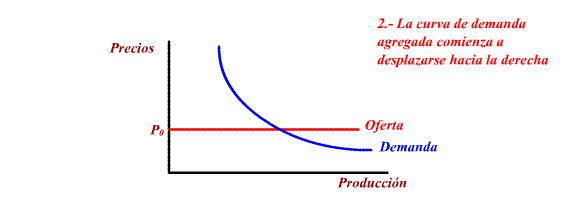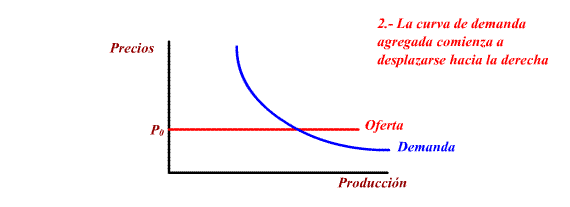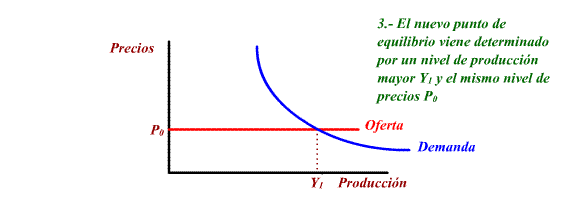
This causes an increase in production
to cover the aggregate demand, which in turn causes an increase
in employement (in this model you can consider la existence
of involuntary unemployment). Prices, in the short term remain
constant.
Fiscal Expansion: increase
of G or decrease of T, cause Aggregate Demand to move right.
Increasing demanded production and the level of employment.
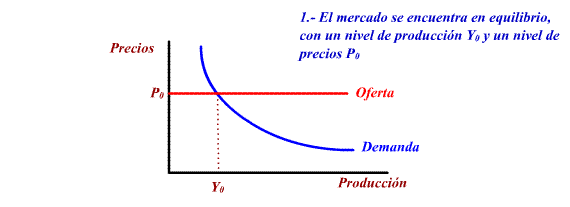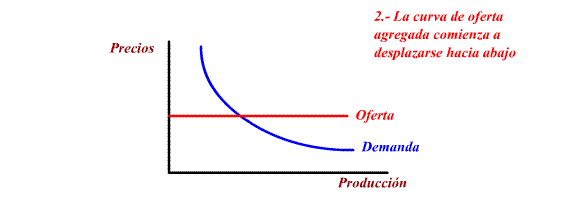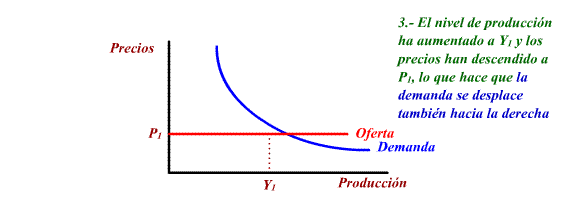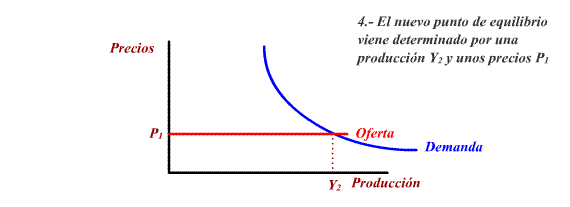
b) Offer policies
These measures manage to move Aggregate
Offer down and towards the right, causing a decrease in prices
and an increase in balanced production and in the level of
employment.
|

