Factors in Cost Advantage
In this lesson and the next one, we will see determining cost factors. We can well say that the relative importance of each will vary in function of the sector, the enterprise and its different activities. To be able to identify the cost determining factors, we can do the following:
• diagnose the cost position of an enterprise, in terms of comprehending why its unit costs are different from those of its competitors.
• Advice the enterprise on how to improve its efficiency in costs.
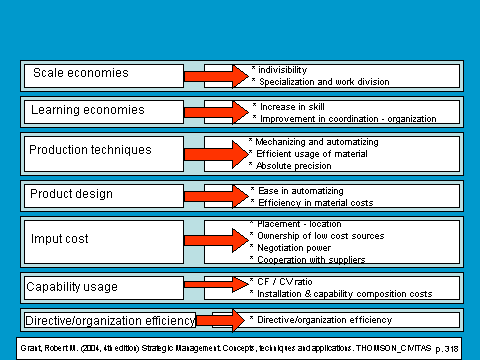
• Scale economies.-
Leadership of great enterprises is produced because of scale economies in any sector we could think of, but it is produced mainly in industrial sectors. Scale economies favour mass production; something not available in small enterprises. Thus, there is a greater production with lower unit costs.
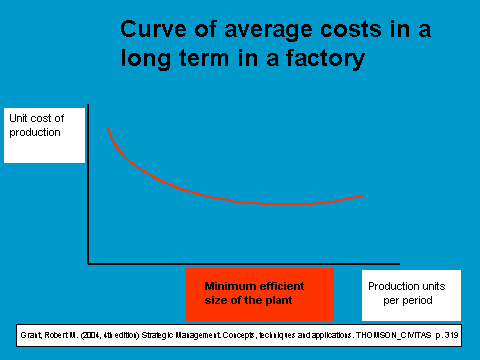
Furthermore, since we are talking about production / manufacturing, we will see the relationship between unit cost of production and the units produced per period in the following chart. Scale economies are mainly related to these processes. The point in which scale economies are at their peak is the so called minimum efficient size of the plant.
b.) Learning economies.-
Learning economies are the effect of repetition. From repetition and the learning capability of the members of the enterprise, we can achieve a costs saving factor mainly due to time. As a result, with a constant repetition of tasks we reduce the time it takes for their execution, productive factors are better coordinated and the experience obtained helps us smooth out any defects. All of this comes together with making the process more efficient.
Learning economies are more useful whenever the productive process or product in question is more complex. Learning takes place in an individual or collective level in the organization. Individually, the improvement obtained is shown in dexterity while the collective aspect is reflected in the improvement of organization routines. An example of learning economies is the leadership of Japan in the flat screen market.

c.) Process technologies and product design.-
To reach a same product / service, different procedures can be developed. Just the same, we can say that a productive process will be better than another one when it achieves the same results but with fewer resources.
The emergence of a new productive process may result in a radical reduction in costs for an enterprise. What it implies for sure is the fact of breaking market structures. This is what happens with IKEA and its flat packages. The furniture by IKEA is placed in flat packages. This enables accessible prices due to the fact that the merchandise is cheaper to store and transport.

Another example in cost reduction in this same manner is found in fast food restaurants. Enterprises with standardized operating systems and franchises have virtually substituted smaller family enterprises dedicated to that sector.

d.) Product design.-
“Designing to manufacture (designing products that are easy to manufacture in stead of being just functional and aesthetic) may offer substantial costs savings, specially when done in conjunction to a new technological process ”.