Factors in Cost Advantage (II)
We continue with what we started in the previous lesson by reviewing the determining factors in cost advantage. As we mentioned before, the relative importance of each one of these factors varies depending on the sector, the enterprise and its different activities.
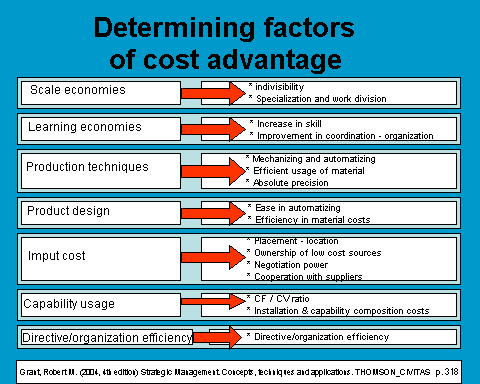
e.) Input cost.-
Inputs are nothing more than resources; productive factors. It would seem logical to think that enterprises in the same sector seize these factors in the same competitive market, and apparently, at the same price. However, it is not so. This provokes, from the beginning of the productive process, important cost differences in enterprises in the same sector. This may happen due to the following reasons:
• differences in the location in the price of factors.
• property of supply sources at a low cost.
• labour which is not indicated.
• Negotiation power.
f.) Capability usage.-
In the case of a factory that has a specific production capability, it is practically constant at short and long terms. In periods of low demand, the productive capability of the factory is well above the described demand. As a result, it shows an increase in the unit cost of production since fixed costs have to be distributed among the small number of manufactured units. In sectors with mostly fixed costs - such as air transport- profits are very sensitive to the variations in demand. In periods of high demand, this can go beyond normal capabilities.
g.) Directive / organization efficiency.-
In this last factor, we refer to the reason why unit costs are different between enterprises in the same sector when their basic cost factors (such as technology, product design, productive process, capabilities, cost of factors, etc.) are very similar, if not the same.
In this case, the difference in costs in global terms comes in what is known as "residual efficiency". This refers to all those costs incurred by enterprises as consequence of organizational routines and the habits of its employees. These are minor and residual costs. However, they are not necessary and the create important differences between two competing enterprises.